Diabetic patients are particularly prone to vascular lesions, and many patients will develop diabetic feet in the later stages. Diabetic foot injuries must be treated in time, otherwise ulcers will develop. So, how do people with diabetes take care of their feet?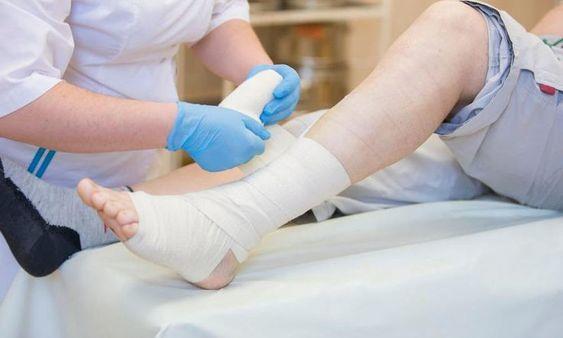
①Prevention:
1. Develop the habit of self-examination:
Before going to bed every night, people with diabetes should carefully examine their feet for redness, swelling, wounds, or discharge. For those patients with poor vision, family members can be asked to help with the examination. At the same time, check whether the foot temperature is uniform by palpation, and pay attention to whether there are tender points to avoid ulcers in the protruding parts of the foot bones.
2. Foot skin care:
Pay attention to the skin care of your feet. Before going to bed every night, soak your feet in warm water for about 10 minutes. Be careful not to overheat the water. After washing your feet, dry them gently and apply alcohol-free skin care products, such as glycerin, to moisturize and protect the skin. When trimming your toenails regularly, keep the trimming line straight and avoid cutting too deeply, which may cause local infection. If you have thick calluses or corns on your feet, you should seek help from a professional doctor and do not treat it yourself.
3. Choice of shoes and socks:
Choosing the right footwear is also crucial for people with diabetes. It is best to wear white, cotton socks, which are breathable and can easily detect bleeding or exudation on the feet. Before wearing shoes, you should check whether there are foreign objects in the shoes and avoid wearing the same pair of shoes for a long time. People with diabetes should avoid walking barefoot indoors and outdoors and limit standing, walking, or running for long periods of time. Also, avoid wearing slippers and high heels as they can cause ulcers to form between the toes or on the bottom of the forefoot. When choosing shoes, it's best to buy them in the evening, when your feet are at their largest. Make sure your shoes are the right size so there is some space between the front of your longest toe and the front edge of the shoe to avoid injuries from friction and pressure.
②Care:
Infected foot wounds in diabetic patients require careful and careful management. During the process of wound debridement, we must pay special attention to maintaining blood circulation in the wound site. Otherwise, excessive debridement may have an adverse effect on wound healing. If the wound area is too large, it may be difficult to completely cover it with the epidermis, and sometimes a skin graft is required, which will undoubtedly prolong the healing time of the wound.
1. When cleaning the wound:
When cleaning a wound, completely remove all calluses around the wound. If the infected wound is under the toenail, we will need to trim part of the toenail to fully expose the base of the wound. During debridement, if necrotic tissue or areas of color change are found, they must be thoroughly removed until healthy and bleeding tissue is exposed. If we encounter sinus tracts, we also need to use alginate dressings to fill them.
2. After cleaning the wound:
After cleaning the wound, we need to rinse it with saline. If the wound is deep or accompanied by sinus tracts, it is recommended to use a syringe to draw hydrogen peroxide for flushing, keep it for two minutes, and then flush it with normal saline.
3. After rinsing:
After rinsing is complete, use alginate dressing to fill the wound to facilitate wound healing. Silicone gel foam dressing can be used to fix the outside. After the dressing is completed, the dressing should be changed once or twice a day according to the exudation of the wound. When the dressing is penetrated, it should be replaced promptly.
Tips:
After debridement of the foot wound, the patient needs to rest in bed with the affected foot elevated. To protect your heels, you can place a pillow under your calves to reduce prolonged contact with the mattress and avoid tissue necrosis. When you have to get out of bed, you can use crutches or a wheelchair to assist.
For more information on Innomed® Super Absorbent Dressing, Refer to the Previous Articles. If you have customized needs, you are welcome to contact us; You Wholeheartedly. At longterm medical, we transform this data by Innovating and Developing Products that Make Life Life easier for those who need loving care.
Editor: kiki Jia

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体