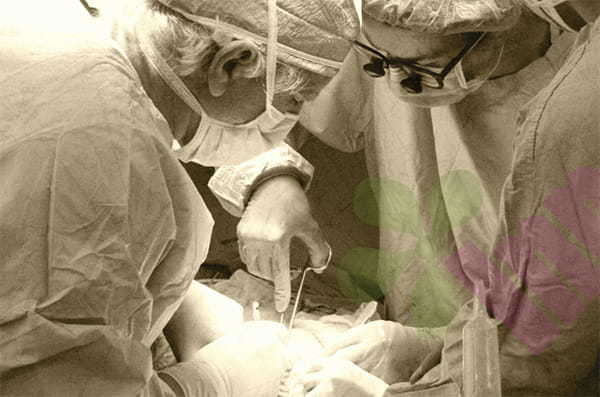
Microbiota refers to the microbial communities that inhabit our skin, mucous membranes, intestines, and other parts of the body. Among these microorganisms, beneficial bacteria, harmful bacteria, and bacteria in between form a complex and delicate ecosystem. In a healthy state, these flora maintain a dynamic balance and maintain our health. However, various factors in life—the abuse of antibiotics, changes in dietary habits, environmental pollution, etc.—may disrupt this balance and lead to bacterial imbalance. This imbalance can have a variety of effects on the body, one of which is affecting wound healing.
A wound is a place where skin and soft tissue have been damaged. The wound healing process is a complex and delicate biological process that requires the synergistic effect of multiple factors. As an important component of the human body's surface and internal environment, bacterial flora plays an important role in the wound healing process.
The importance of skin flora in wound healing
Skin, as the largest organ of the human body, is not only our first line of defense against the outside world but also bears the important task of maintaining body fluid and electrolyte balance. A healthy body has some immunity to commensal flora, but when the immune system is weakened or the number of flora increases abnormally, the risk of infection increases.
Why do chronic wounds form?
Slough and necrotic tissue in the wound provides a breeding ground for bacteria. If the infection and inflammation are further aggravated, the wound condition will be further worsened. In addition, vascular lesions and poor circulation caused by hyperglycemia, venous ulcers of the lower limbs, etc. can also cause An important factor in chronic wounds is that when there are cysts, abscesses, sinuses, etc. in the wound and poor drainage, the wound healing process will also be hindered.
How to treat chronic wounds?
When treating chronic wounds, the first thing we need to do is clean the wound. This includes removing black scabs, slough, pus, and other necrotic tissue, using cotton swabs, tweezers, scissors, and other tools for cleaning. For tightly adherent slough, ointment can be used to dissolve and liquefy the wound to keep it flat and clean, allowing fresh granulation tissue to be exposed. Since chronic wounds are often accompanied by infection and inflammation, it is necessary to strengthen dressing changes and use herbal ointments or Silver Ion Dressing for antibacterial disinfection to control inflammation. During this process, avoid overusing antibiotic ointment or spreading antibiotic powder on the wound. This approach may force the wound to form a dry scab before the granulation has completely flattened out, which may lead to the accumulation of pus under the dry scab and involve necrosis of normal tissue.
The correct approach is to promote wet healing of the wound through appropriate antibacterial treatment and moisturizing care, provide a moist environment for the growth of granulation tissue, and accelerate the wound healing process.
For more information on Innomed®Silver Ion Dressing, Refer to the Previous Articles. If you have customized needs, you are welcome to contact us; You Wholeheartedly. At longterm medical, we transform this data by Innovating and Developing Products that Make Life Life easier for those who need loving care.
Editor: kiki Jia

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体