Children are naughty by nature, so injuries and accidents are inevitable. Because some parents lack parenting experience and medical knowledge, wounds will increase the risk of infection. Wrong treatment of wounds will also affect children's health, so learning how to handle them correctly Wounds are very important. This article will introduce some knowledge about children's wound care. Please follow me to take a look.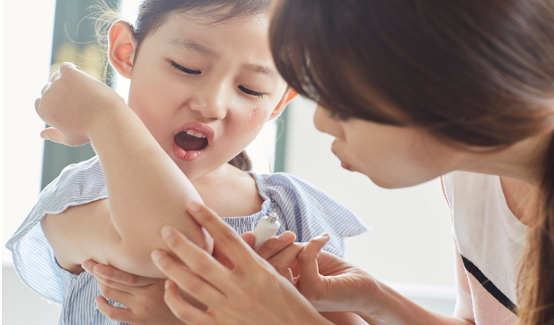
First, understand the characteristics of children's skin:
Compared with adult skin, there are great differences in the skin structure, barrier function, and skin composition of children's skin. Although the skin of a full-term baby is structurally similar to that of an adult, the dermis of a baby is only a little over half as thick as that of an adult. This thickness increases with age, but pediatric patients often have much more delicate skin than adults. Pediatric patients are injured for different reasons than adults. Pediatric patients are more likely to have acute trauma, such as traumatic accidents and burns. Chronic wounds are rare but may result from medical device-related pressure or friction and shear.
Nursing assessment of children's wounds :
As with adults, the need for a thorough physical assessment is critical to developing an effective treatment plan; this includes an assessment of wound size, tissue characteristics, exudate levels, and signs of infection, a complete assessment of the peri-wound area, and periodic reassessment to determine whether healing or if management strategies must be changed.
Are the stages of wound healing in children?
In the first few seconds after a skin injury, local blood vessels narrow reflexively and produce bioactive substances - platelets, which adhere to the wound area and close the damaged blood vessels. The coagulation system is activated and the bleeding is stopped. Bleeding in healthy children stops on its own within 15 minutes. Continues for 3 days from the moment of injury. Inflammation manifests as pain, redness, and localized heat. In addition, within two hours, the wound develops swelling in the form of a tumor. Leukocytes migrate to the injured area 2-4 hours after injury. They absorb foreign matter and clean microbial wounds. healing phase. Start 3-5 days after injury. Bioactive substances reach damaged tissues and repair blood vessels and skin tissues. Epithelialization stage. Start 2 weeks after injury. The marks of the wound become pale and a scar forms. The epithelialization phase may be delayed if bacteria are present in the wound.
How to choose dressings for different wounds?
Wound management in pediatric patients has several key goals, including relieving pain, preventing wound infection, and minimizing scarring.
Commonly used wound dressings :
Different types of dressings have different effects on wounds, so understanding the functions of commonly used dressings has a great impact on faster wound healing. Here are some commonly used dressings:
1. Hydrocolloid Dressing Ultra-thin:
This dressing is very comfortable and compliant to use. It is suitable for superficial skin damage and can relieve the pain of the wound. The most important thing is that it can provide the wound with a slightly acidic airtight space that is conducive to wound healing. It can also be flexible and casual Cut to size.
2. Silicone Foam Dressing Non Bordered:
This dressing is suitable for wounds with a lot of exudates. It adds a layer of mesh silicone gel to completely cover the foam core and adhesive film, making the original non-stick foam core sticky and making silicone gel foam dressing. The patch adheres more firmly to the wound. At the same time, the contact between the mesh silicone layer and the wound is more gentle, and the wound will not stick after removing the silicone foam applicator, which is very friendly to children's skin.
3. Silicone Scar Dressing Tubular:
This dressing should be used 2 weeks after the wound has healed. Pay attention to observe that the wound is not red, swollen, or bleeding. It is used to prevent scars. It is suitable for operations, burns, lacerations, and various types of keloids and hypertrophic scars. Gel-type silicone is very malleable and suitable for areas with irregular skin or active children. When the gel is applied to the skin, it dries quickly and forms a breathable, transparent, and waterproof layer to protect against chemical, physical and microbial intrusion. Silicone scar gel has scar-improving properties due to the hydration of the scar and hydration provides better collagen tissue during the healing phase. It smoothes, softens, and smoothes scars, relieves itching, and reduces scar-related discoloration.
Correct treatment of children's wounds :
1. Hemostasis: If the wound is bleeding, press with clean gauze for 10 minutes to stop the bleeding.
2. Cleaning: Rinse the wound with clean water to remove dirt such as sand and debris.
3. Scratches and abrasions: Rinse the wound with clean water or physiological monitoring water, wipe the wound with povidone-iodine, and apply Hydrocolloid Dressing Ultra-thin. If the area is large or deep, seek medical attention.
For more information on Innomed® Silicone Foam Dressing Non Bordered, refer to the previous articles. If you have customized needs, you are welcome to contact us; we will serve you wholeheartedly.
At Longterm Medical, we transform this data by innovating and developing products that make life easier for those who need loving care.
Editor: kiki Jia
Date: January 17, 2023

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体








