A skin ulcer is an open, pit-like wound on the skin that is often difficult to heal. If left untreated, it can lead to more serious problems. Skin ulcers are caused by factors such as external trauma, poor blood circulation, or continued stress. The legs are the most common site of disease, especially in the elderly.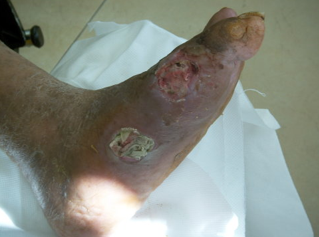
Symptoms of skin ulcers:
Symptoms of skin ulcers include pain, swelling, itching, burning, rash, redness, color change, dry skin, scaling, scab formation, swelling of the skin around the ulcer, tenderness, exudate, odor, etc. Common types of ulcers include arterial ulcers, neuropathic ulcers, and venous ulcers. In addition, there is a pressure injury, also known as a bedsore or pressure sore, which is damage to the skin and deep tissue caused by prolonged pressure.
Causes of skin ulcers:
The causes, symptoms, and treatments of skin ulcers are important in preventing and treating this common condition. With correct care and preventive measures, the incidence of skin ulcers can be effectively reduced and the patient's pain relieved. For long-term wheelchair users, such as paraplegics, pressure ulcers may be difficult to detect due to limited mobility. This condition may prevent pressure ulcers from being treated promptly, leading to more serious consequences such as pressure ulcer ulceration, infection, and even damage to deeper muscle and bone tissue. If pressure ulcers are not treated promptly, serious wounds can take a long time to heal.
Pressure ulcers can develop for a variety of reasons, some of which are intrinsic, such as circulatory disorders such as the effects of atherosclerosis, diabetes, renal failure, hypertension, etc.; venous insufficiency, lymphedema, and some Inflammatory diseases, smoking, and genetic factors, among others. Other causes such as staying in the same position for long periods of time, poor nutrition, and certain medications can also cause skin damage. In addition, some systemic diseases such as heart disease, sickle cell anemia, inflammatory bowel disease, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure may also increase the risk of skin damage.
Treatment and prevention of skin ulcers:
Treatment of skin ulcers depends on the specific cause and severity and may require a combination of medications, surgery, home self-care, and preventive measures. At the same time, different treatment plans are required for different types of ulcers and symptoms. The key to preventing skin ulcers is to reduce pressure and friction, keep the skin clean and moisturized, and enhance nutrient intake and blood circulation. For individuals who are bedridden or have limited mobility, regular posture changes and increased physical activity are also important measures to prevent pressure ulcers.
When treating skin ulcers, the goal is to relieve the patient's pain and speed recovery and healing of the wound. Each patient's treatment plan needs to be tailored based on their health, disease, and ability to self-care for their wounds. Common treatments include anti-infective therapy, local wound management such as debridement, application of dressings, creams/ointments, and antimicrobials; anticoagulant or antiplatelet medications to prevent thrombosis; compression therapy such as the use of compression stockings or bandages; Orthotics or prosthetics to help restore or enhance the ability to perform activities of daily living.
For those wounds that are difficult to heal, longer treatment may be needed, but the key is to eliminate factors that affect wound healing, such as managing complications, providing adequate nutrition, and improving circulation. If you are unfortunate enough to suffer from skin ulcers, especially ulcers on the feet and lower limbs, home self-treatment is a viable option. After all, skin ulcers are common in these areas, so treating them with skin and foot care is a priority. Especially for people with diabetes, regular skin and foot checks are essential. Early detection and treatment can help prevent infection and ulcers from getting worse.
For foot or leg ulcers, daily cleaning and care is essential. Washing the injured area with warm water and mild soap will not only remove dead skin and local exudates and debris but also promote skin metabolism. After cleansing, dry your skin gently, especially between your toes, avoiding excessive rubbing.
Routine self-examination is also key to preventing and treating ulcers. Check your legs and feet for abrasions, cracks, cuts, blisters, etc. Pay special attention to local redness, swelling, ingrown toenails, corns, etc. If necessary, use a mirror or ask a family member to help check hard-to-reach areas.
Moisturizing is key to healthy skin, especially for the lower limbs and feet. Apply emollient 1-2 times a day, it is recommended to use a moisturizing product such as lanolin. Avoid using emollient on open wounds, and be careful not to use lotion between the toes.
The timing of trimming your toenails is also important. Toenails are softer after bathing. Trimming them at this time can reduce damage to surrounding tissues. Use a nail file to polish carefully, keeping your nails flat and not too deep around the edges.
For diabetic patients or people with existing skin ulcers, it is very necessary to go to the hospital for regular examination and follow-up. If you have problems such as corns and calluses, please do not deal with them on your own and seek professional medical help promptly.
For more information on Innomed® Silicone Foam Dressing, Refer to the Previous Articles. If you have customized needs, you are welcome to contact us; You Wholeheartedly. At longterm medical, we transform this data by Innovating and Developing Products that Make Life Life easier for those who need loving care.
Editor: kiki Jia
Date: January 30, 2023

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体








