An uncle in his 60s asked for help in the group: more than a year after the operation, he found that the stomach next to the stoma was bulging. It was obvious when he stood up and disappeared when he was lying down. What happened?
In fact, this is one of the most common complications after ostomy - parastomal hernia. Up to 78% of people will have parastomal hernia after ostomy surgery, usually within two years after surgery.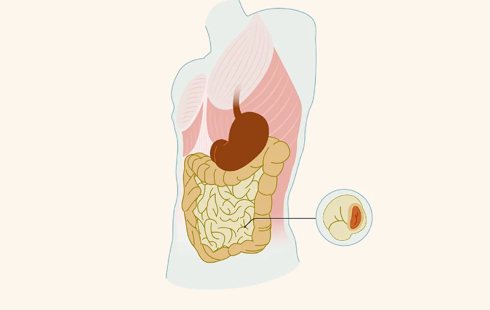
What is a parastomal hernia?
A parastomal hernia is a type of incisional hernia of the abdominal wall adjacent to or next to a stoma, which is an abnormal protrusion of abdominal contents through a defect in the abdominal wall caused by an enterostomy. The physical activity of stoma patients is affected by many factors. This is after an abdominal stoma . Due to various factors, the abdominal wall tissue next to the stoma is weak and defective, and other tissues in the abdominal cavity, such as the intestine, protrude from the weak place causing the abdominal wall next to the stoma to bulge. The complications of parastomal hernia are as high as 30%-50%, especially in the elderly.
Early manifestations of parastomal hernia:
In the early stage of parastomal hernia, the patient has no obvious symptoms, only slight discomfort or a feeling of bulging in the stoma appendix, but if there are no effective treatment measures, the hernia mass will gradually increase accompanied by abdominal pain and abdominal distension, protruding from the skin surface The parastomal hernia will also affect the fit with the ostomy bag, easily lead to leakage, resulting in dermatitis around the stoma, and in severe cases, it will aggravate the parastomal hernia and cause intestinal obstruction, affecting the quality of life.
Causes of parastomal hernia:
1. Factors related to patients: such as obesity, old age, malnutrition, malignant disease, obstructive pulmonary disease, urinary tract obstructive disease, application of hormones, etc.
2. Factors related to surgery: type of stoma, location of stoma, size of stoma aperture, etc. It is related to the choice of stoma location and stoma technique. Most scholars believe that the parastomal hernia is most likely to occur through the pararectus stoma and the stoma through the abdominal incision. The transects stoma can reduce the occurrence of parastomal hernia. In addition, the stoma opening is too large, and the stoma is located at the laparotomy incision, which is easy to induce the occurrence of a hernia.
3. Postoperative factors: parastomal hernia infection, other abdominal complications, postoperative abdominal distention or ascites, radiation therapy, weight gain, early or premature labor, etc.
What are the general symptoms?
The main manifestation of parastomal hernia is the bulging of the abdominal wall next to the stoma, which increases after standing, walking, and exertion. There are no symptoms in the early stage, but as the course of the disease prolongs, the parastomal hernia will gradually become larger.
Generally, it will not be affected when it is not serious in the early stage, but it will affect daily life and cause the chassis of the ostomy bag to be poorly pasted and leaked, increasing the difficulty of stoma care. In addition, in severe cases, it will cause intestinal adhesions, abdominal pain, abdominal distension, and even intestinal incarceration or narrow necrosis, which is life-threatening.
Why do parastomal hernias occur?
The stoma surgery itself will cause a local abdominal wall defect, and it is difficult to make the size of the stoma hole just right. If the hole is too small, the stoma will be narrow, and defecation will be difficult. If it is too large, a small gap will be formed next to the stoma. The peristalsis of the bowel is persistent and has a strong impact on the tissue around the stoma. Over time, the original air attack next to the stoma will become larger, which will lead to the occurrence of para hernia.
In addition, factors such as severe cough, difficulty in defecation, and increased intra-abdominal pressure such as ascites can also lead to a parastomal hernia. In addition, malnutrition, postoperative wound infection at the stoma site, and improper surgical procedures can increase the incidence of parastomal hernias.
Especially in the elderly, as well as significant weight loss after surgery, the abdominal wall will relax, fat will become thinner, and the incidence of parastomal hernia will also increase.
So, how can we prevent and deal with it after we are discharged from the hospital?
First, for patients with malnutrition, nutritional support needs to be strengthened before and after surgery; for obese patients, weight can be properly controlled to avoid excessive weight loss;
Secondly, the use of an abdominal belt can reduce abdominal pressure, especially when coughing and sneezing, which is currently an important way to prevent stoma hernia.
In addition, the prevention of parastomal hernia, but also avoid excessive force, avoid lung infection, and severe cough.
Finally, if the parastomal hernia is severe, the hospital's treatment method is surgical repair, but the recurrence rate is still relatively high. Therefore, the most important thing for parastomal hernia is prevention.
You don't have to be too nervous because of this. By doing the above prevention methods in advance, you can prevent parastomal hernias as much as possible.
For more information on Innomed® ostomy bags, refer to the previous articles. If you have customized needs, you are welcome to contact us; we will serve you wholeheartedly.
At Longterm Medical, we transform this data by innovating and developing products that make life easier for those who need loving care.
Refer to:
1. Feng Man. Construction and application of parastomal hernia prevention and nursing program for enterostomy patients [D]. Jiangsu University, 2021. DOI: 10.27170/d.cnki.gjsuu.2021.001733.
2. Zhu Lixia, Jiang Wujia, Hua Jianhong, Jiang Xiaoqin. Research progress on the correlation between parastomal hernia and physical activity in patients with stoma[J]. General Nursing, 2021,19(30):4221-4223.
Editor: kiki Jia
Date: August 5, 2022

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体








