Myofibroblasts are a type of cell that plays an important role in wound healing. They act as a scaffold and support during wound healing, helping in tissue repair and regeneration.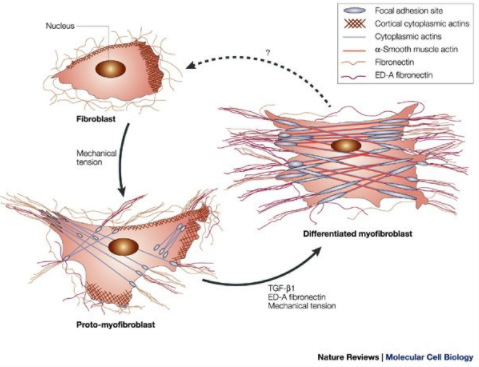
What are myofibroblasts?
Myofibroblasts are highly active cells that differentiate into muscle cells and produce large amounts of matrix components such as collagen and elastin during injury and tissue remodeling. Myofibroblasts can also produce a variety of cytokines and growth factors, such as transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), matrix metalloproteinases (MMP), etc. These factors are involved in the repair and reconstruction of muscle tissue.
How to activate myofibroblasts in chronic wounds?
Activation of myofibroblasts plays a key role in chronic wound repair. Here are some ways to activate myofibroblasts in chronic wounds:
1. Inflammation: Inflammation can activate myofibroblasts, so in the treatment of chronic wounds, the use of drugs with anti-inflammatory effects, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and steroids, can reduce inflammation, thereby reducing muscle formation. Activation of fibroblasts.
2. Growth factors: Many growth factors, such as transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), etc., can promote the activation and proliferation of myofibroblasts. In chronic wound therapy, growth factors can be used to activate myofibroblasts and promote wound repair.
Physical stimulation: Physical stimulation, such as pressure, temperature, and electrical stimulation, can activate myofibroblasts. In chronic wound therapy, physical stimulation can be used to activate myofibroblasts and promote wound repair.
3. Extracellular matrix: Extracellular matrix (ECM) is the matrix component around myofibroblasts, which can affect the activation and proliferation of myofibroblasts. In chronic wound therapy, ECM components, such as collagen and elastin, can be used to activate myofibroblasts and promote wound repair.
It should be noted that the activation of myofibroblasts can promote the repair of chronic wounds, but can also lead to hyperactivation and fibrosis. Therefore, in actual treatment, it is necessary to select the appropriate treatment method according to the specific situation and pay attention to controlling the degree of activation to achieve the best therapeutic effect.
How to reduce myofibroblast activity to prevent or treat hypertrophic scars?
Hypertrophic scars or keloids are usually due to excessive activation and proliferation of myofibroblasts. Currently, the use of Silicone Scar Dressing can reduce scarring. The mechanism of action of silicone, including moisturizing and airtight environment, stimulates the protective properties of healthy skin and reduces myofibroblast activity and collagen formation. In addition, reduced scar edge tension also reduces the activity of myofibroblasts, as these cells respond to mechanical forces. With regard to corticosteroids, it has been shown to inhibit the expression of TGF-β1, thus inhibiting the proliferation and favoring the apoptosis of myofibroblasts. Some keloids require surgical excision, which completely removes the myofibroblasts and reduces scar formation. When surgically removing a keloid, care needs to be taken not to remove too much tissue to avoid post-operative complications.
What is the process of myofibroblasts in wound healing?
During wound healing, myofibroblasts first appear at the wound edge and form a layer of cells on the wound surface. These myofibroblasts are highly proliferative and differentiated and can divide into new myofibroblasts and differentiate into collagen and other extracellular matrix components. These components form the scaffold and foundation, providing support for neovascularization and entry of epithelial cells. Myofibroblasts can also produce growth factors and cytokines, such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), and epithelial growth factor (EGF), which can promote wound repair and regeneration. In addition, myofibroblasts can also produce hyaluronic acid, which is an important mucopolysaccharide, which helps in the adhesion and sealing of wounds and prevents wound damage from external factors.
In conclusion, myofibroblasts play an important role in wound healing. Through the study of myofibroblasts, we can better understand the process of wound healing and lead to new therapeutic methods for wound healing.
For more information on Innomed® Silicone Scar Dressing, refer to the previous articles. If you have customized needs, you are welcome to contact us; we will serve you wholeheartedly.
At Longterm Medical, we transform this data by innovating and developing products that make life easier for those who need loving care.
Editor: kiki Jia
Date: April 6, 2023

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体








