As one of the most sophisticated organs in the human body, the hand undertakes complex functions such as grasping, touching, and operating. When an accident causes a hand injury, correct first aid treatment can not only relieve pain but also lay the foundation for subsequent functional recovery. This article will start with the anatomical structure of the hand and systematically explain the key points of first-aid treatment for hand injuries.
First, understand the anatomy of the hand:
Skeleton: The skeleton of the hand is composed of 8 carpal bones, 5 metacarpal bones, and 14 phalanges (3 for each finger and 2 for the thumb). This truss structure not only ensures the stability of the hand but also gives it flexible bending ability. Special attention should be paid to the functional position of the hand: the wrist joint is dorsiflexed 20-25°, the thumb is abducted to the palm, and the other four fingers are in a half-fist shape. This posture can maintain the function of the hand to the maximum extent and is the key position to be maintained during first aid bandaging.
Muscles: The muscles of the hand are divided into extrinsic muscles (extension of the forearm tendons) and intrinsic muscles (muscles in the palm). Extrinsic muscles are responsible for gross movements such as grasping, while intrinsic muscles control fine movements such as writing. It is worth noting that damage to the thenar muscles (thumb opposition muscles) and hypothenar muscles will directly affect the finger opposition function of the hand and needs to be evaluated during the examination.
nerve :
①Nerve distribution: The median nerve innervates the palmar thumb, index finger, middle finger, and radial half of the ring finger, the radial nerve innervates the base of the palm on the back of the hand, and the ulnar nerve innervates the little finger and ulnar half of the ring finger. Nerve damage can lead to sensory and motor dysfunction.
② Vascular system: The radial artery and ulnar artery form the superficial palmar arch and the deep palmar arch in the wrist. This dual blood supply system ensures good compensatory ability of the hand, but the blood vessels in the palm are relatively small and vasospasm is prone to occur in case of trauma.
Ligaments and joints: The interphalangeal joints and metacarpophalangeal joints are stabilized by collateral ligaments, while the wrist joints are protected by a triangular fibrocartilage complex composed of multiple ligaments. Damage to these structures can lead to joint instability and affect hand grip strength.
How do we examine hand injuries?
Normal skin is pink, paleness indicates insufficient arterial blood supply, and cyanosis may be due to venous reflux obstruction. Press the nail bed for 2 seconds and then release it. Normally, it should return to redness within 1-2 seconds. Delayed recovery indicates circulatory disorders. The patient's range of motion is compared with the healthy side. Squeeze along the long axis of the limb, and increased pain indicates possible fractures. Tap the nerve course area, and radiating pain indicates nerve repair or regeneration. Assess whether the radial and ulnar artery communicating branches are patency to ensure blood supply to the hand after unilateral artery ligation.
First aid steps for hand injuries :
The first step is hemostasis and debridement :
Cover the wound with sterile gauze and apply pressure for 15 minutes. Avoid opening the wound frequently for inspection. Use only when large blood vessels in the limbs are injured. Mark the time and relax for 5 minutes every hour. Use a syringe to flush the wound at low pressure to remove foreign matter. Do not use iodine to flush the wound directly.
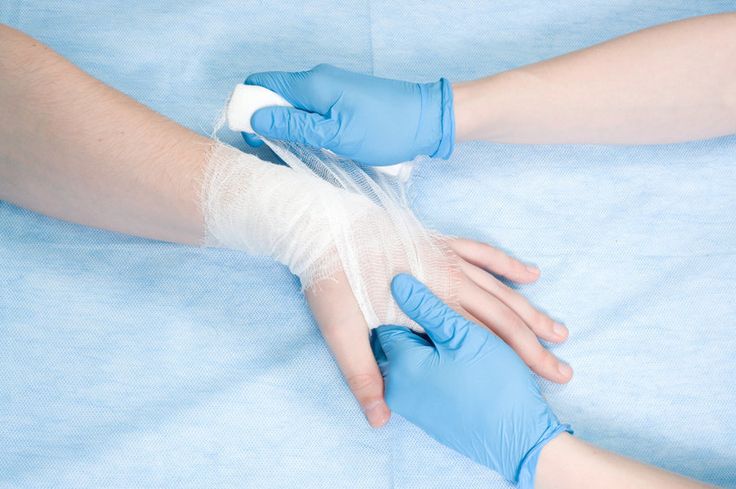
Step 2 Wound dressing :
For wounds on the palm side , the "8" bandage method can be used to maintain the dorsiflexion position of the wrist joint. For wounds on the fingertips, butterfly tape is used to align the wound edges, and sterile dressings are used to wrap the wounds. The fingertips are left empty to observe the blood circulation. For wounds on joints, aluminum core splints are used to fix them in the functional position, and the length exceeds the upper and lower bone segments of the joint.

Hand wounds heal in three stages:
Inflammatory phase (0-3 days): Platelets aggregate to stop bleeding, neutrophils remove foreign matter
Proliferation phase (3-21 days): Fibroblasts synthesize collagen and capillaries are regenerated
Remodeling period (21 days to 1 year): collagen fiber reorganization, scar softening
Understanding this process can help to properly treat hand wounds, avoid excessive activity that affects collagen deposition, and conduct rehabilitation training to prevent adhesions. When encountering serious trauma, contact a specialist in time, because microsurgery technology can regenerate severed fingers and give dexterous hands a new life.
For more information on Innomed®Hydrocolloid Dressing, refer to the Previous Articles. If you have customized needs, you are welcome to contact us; You Wholeheartedly. At longterm medical, we transform this data by Innovating and Developing Products that Make Life easier for those who need loving care.
Editor: kiki Jia

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体








