Gastric perforation is a surgical emergency in which the continuity of the entire structure of the gastric wall (from the mucosal layer to the serosal layer) is interrupted, resulting in the infiltration of gastric contents into the abdominal cavity. The core cause is progressive gastric ulcer (accounting for more than 70%), and other causes, such as malignant tumors, trauma, and drug damage, can also cause it. It is particularly important to note that the initial damage depth of a gastric ulcer can reach the muscular layer. Under the influence of overeating, alcohol stimulation, etc., the weakly defended serosal layer is easily penetrated, eventually forming a perforation.
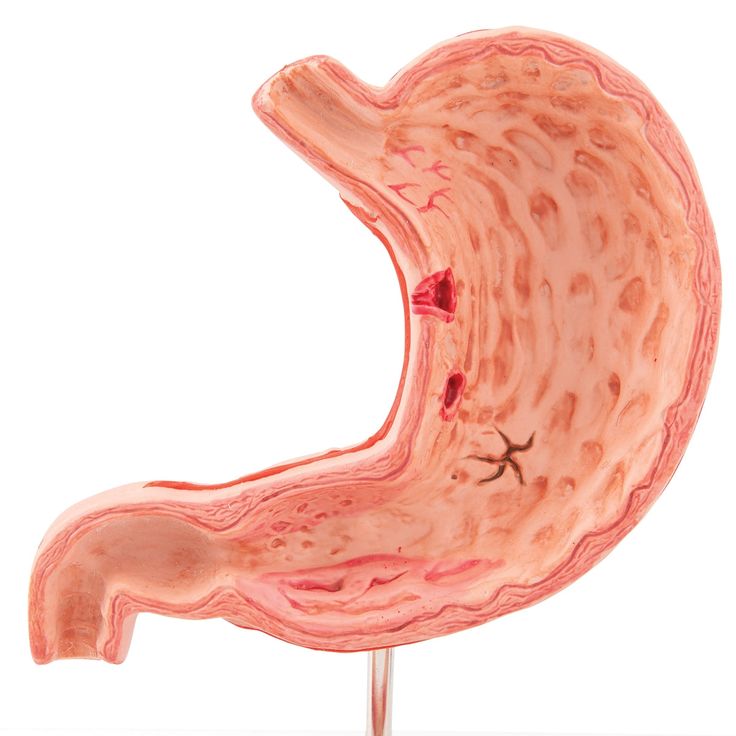
Anatomy of the stomach :
Dynamic morphological characteristics:
Double-zone double-orifice structure: bounded by the cardia (connected to the esophagus) and the pylorus (connected to the duodenum); the upper edge of the stomach has an angled notch on the lesser curvature, and the lower edge of the stomach is arched in the greater curvature
Four parts: cardia, vault-shaped gastric fundus, main gastric cavity, pyloric part (including pyloric canal and pyloric antrum)
Layered defense mechanism:
Mucous membrane: the innermost layer, in direct contact with food and digestive juices, responsible for secretion and absorption, and the most fragile.
Submucosa: Rich in blood vessels and nerves, it supports the mucosa.
Muscular layer: composed of smooth muscle, responsible for peristalsis to push food.
Serosa: The outermost smooth protective membrane that faces the abdominal cavity.
A perforation means that the wall is completely pierced, the fortress is lost, and the contents leak out.
Common causes of gastric perforation :
1. Progression of primary lesion
Ulcer exacerbation: Deep ulcers penetrate the muscle layer under the continuous erosion of gastric acid (accounting for 85% of perforation cases)
Tumor invasion: gastric cancer tissue necrosis leading to perforation, irregular pain, and ineffective acid-suppressing drugs
Drug damage: NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandins and weaken the mucosal repair ability
2. Mechanical rupture
Pressure surge: Overeating causes stomach volume to exceed the limit (Laplace's law: tension ∝ pressure × radius)
Traumatic path: direct penetration by sharp objects > blunt impact injury (the greater curvature of the stomach is more prone to rupture)
3. Infection and barrier disruption
Helicobacter pylori (Hp) destroys mucosal integrity through an inflammatory cascade reaction, laying the pathological basis for perforation.
Clinical manifestations:
1. Characteristics of abdominal pain
Onset: Sudden, sharp pain in the upper abdomen → diffuse pain in the entire abdomen (gastric acid chemical peritonitis)
Radiating pain: pain referred to the shoulder due to diaphragmatic irritation; right lower abdominal pain (contents seeping down the paracolic gutter)
2. Two-stage shock
Early neurogenic shock: pain-induced pallor/cold sweat/rapid pulse
Late septic shock: bacterial peritonitis causing high fever/impaired consciousness/anuria
3. Classic triad of signs
Board-like abdomen (muscle guarding), tenderness and rebound tenderness, loss of liver dullness (free air sign under the diaphragm)
Key diagnostic technology combination :
1. X-ray upright chest and abdominal films: crescent-shaped translucent area below the diaphragm (confirmed free gas)
2. Ultrasound/CT: localize peritoneal effusion and guide diagnostic puncture
3. Abdominal puncture: turbid digestive fluid containing food residues is extracted (amylase↑)
The four golden principles of first aid
1. Posture control: Left lateral decubitus → limit the spread of gastric contents into the abdominal cavity
2. Pressure relief: nasogastric tube continuous negative pressure suction (decompression volume > 500ml/hour)
3. Anti-infection defense line: third-generation cephalosporins + anti-anaerobic drugs (such as ceftriaxone + metronidazole)
4. Metabolic support: intravenous nutrition to maintain positive nitrogen balance (TPN regimen)
For more information on Innomed®Hydrocolloid Dressing Ultra-thin, refer to the Previous Articles. If you have customized needs, you are welcome to contact us; You Wholeheartedly. At longterm medical, we transform this data by Innovating and Developing Products that Make Life easier for those who need loving care.
Editor: kiki Jia

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体








