The choice of wound dressing directly impacts the healing process. While the right dressing can promote wound recovery, an inappropriate choice can delay healing and even lead to complications. Modern wound care emphasizes individualized dressing selection based on wound characteristics. Below are common dressing application scenarios and selection guidelines.
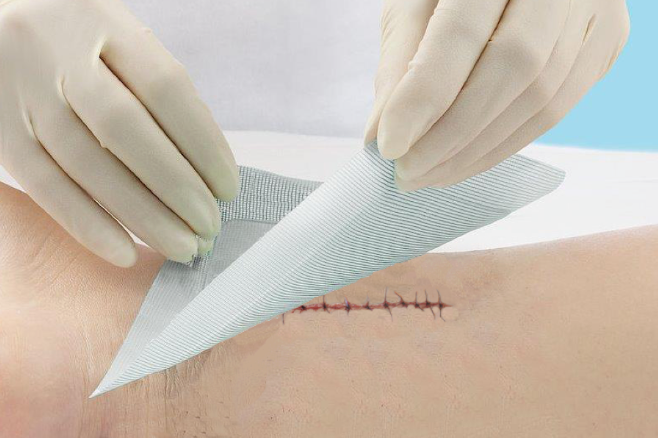
How to identify wound characteristics?
Before selecting a dressing, a comprehensive assessment of the wound is required. Observe the color of the wound base, which can be divided into red (healthy granulation tissue), yellow (dead flesh), black (necrotic tissue), or mixed. Measure the size, depth, and extent of the wound. Assess the amount of exudate, which can be divided into no exudate, small amount (dressing changed once a day), medium amount (dressing changed twice a day), or large amount (dressing changed more than three times a day). Pay attention to the condition of the skin around the wound, whether there is maceration, eczema, or redness and swelling. Understand the cause of the wound, whether it is a surgical wound, pressure injury, or diabetic foot ulcer. Consider the patient's overall condition, including nutritional status, mobility, and underlying diseases.
What are alginate dressings suitable for?
Alginate dressings are made from seaweed extract and form a gel-like substance when exposed to exudate. They are suitable for wounds with moderate to heavy exudate. For cavitary wounds or sinus tracts, alginate dressings can fill dead space and absorb large amounts of exudate. When used on bleeding wounds, alginate has a hemostatic effect. The dressing should typically be changed daily, and should be changed promptly when saturated. When removed, rinse with saline to avoid damaging new tissue. They are not suitable for dry wounds or those with minimal exudate, as they may adhere to the wound and cause secondary damage.
What are the characteristics of silver-containing silicone gel foam dressing?
Silver-containing dressings combine the antimicrobial effects of silver ions with the absorbent properties of foam dressings and are suitable for wounds at high risk of infection or those already infected. Silver ions are effective against a wide range of bacteria, including drug-resistant strains. The silicone gel layer does not stick to the wound, is painless to change, and protects the surrounding skin. They are suitable for wounds at high risk of infection, such as diabetic foot ulcers, burns, and pressure injuries. They can typically be used for 3-7 days, depending on the amount of exudate. They are contraindicated in those allergic to silver, and long-term use requires monitoring for symptoms of argyria.
What wounds are suitable for superabsorbent dressings?
Superabsorbent dressings have a strong fluid absorption capacity and are suitable for heavily exuding wounds, such as those with lymphorrhea and chronic exuding wounds. Their unique structure traps exudate in the core of the dressing, keeping the skin around the wound dry. They are suitable for situations requiring extended change intervals; some can last for several days without change. For wounds requiring odor control, some superabsorbent dressings incorporate an activated carbon layer. They are not suitable for dry or lightly exuding wounds, as excessive drying can impair healing.
What are the advantages of negative pressure wound therapy?
Negative pressure wound therapy uses a closed system to generate negative pressure on the wound surface, promoting drainage of exudate and the growth of granulation tissue. It is suitable for complex wounds such as acute trauma, postoperative wounds, and pressure injuries. It can reduce the number of dressing changes and the nursing workload. It promotes local blood circulation and accelerates the removal of necrotic tissue. However, it requires professional operation and regular replacement of the collection canister and dressing. It is not suitable for actively bleeding wounds, malignant wounds, or untreated osteomyelitis.
How to combine different dressings?
Complex wounds may require a combination of dressings. For deep cavity wounds, an alginate dressing can be used initially to fill the wound, followed by a covering foam dressing. For infected wounds, silver-containing dressings can be used initially to control infection, followed by a transition to other dressings to promote healing. For heavily exuding wounds, a superabsorbent dressing can be used initially to manage exudate, and then a different dressing can be used once exudate decreases. Negative pressure therapy can be used in conjunction with other dressings to enhance therapeutic efficacy.
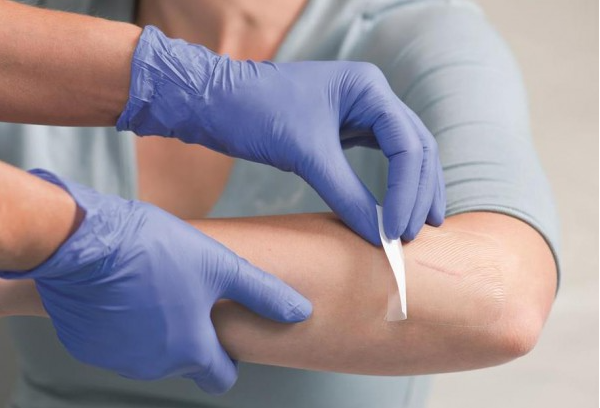
What should I pay attention to when changing the dressing?
Before changing the dressing, wash your hands and prepare the necessary materials. Gently remove the old dressing. If it is sticking, moisten it with saline solution before removing it. Observe the wound and record any changes. Clean the wound with saline solution to remove necrotic tissue and residual dressing. Select an appropriate dressing based on the wound's condition. Position the dressing correctly, completely covering the wound and extending 2-3 cm beyond the edges. Secure the dressing to avoid tightening it and restricting blood circulation. For more information on Innomed® Negative Pressure Dressing, refer to the Previous Articles. If you have customized needs, you are welcome to contact us; You Wholeheartedly. At longterm medical, we transform this data by innovating and developing products that make life easier for those who need loving care.
Editor: kiki Jia

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体








