What are barbs, and why do they form?
Hangnails, medically known as paronychia, are small, triangular pieces of skin around the fingernails that have peeled off and separated from the nail bed. They are especially common in the dry autumn and winter seasons, or after frequent handwashing, contact with detergents, or use of alcohol-based disinfectants, which exacerbate the loss of moisture and oil from the stratum corneum, causing this skin to lose elasticity and become fragile. Hangnails are essentially a signal of dehydrated and dry skin.
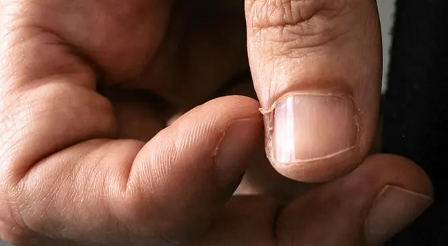
What are the risks of tearing or pulling off the barbs directly?
Many people's first reaction to seeing a hangnail is to tear it off or bite it off for immediate relief, but this action carries significant risks. The most common risks are pain and bleeding. The connection between a hangnail and the underlying skin is often deeper than it appears; tearing it can involve the healthy skin tissue below, creating a tiny tear. The pain from this tear far exceeds that of the hangnail itself. Improper handling can lead to deeper wounds and infections. Pulling hard can easily enlarge the wound, forming a deeper crack. Since fingers come into contact with countless objects daily, bacteria and fungi can easily enter through this open wound, causing paronychia, an acute infection of the soft tissue around the nail. Symptoms include redness, swelling, heat, and severe throbbing pain on one side or at the base of the nail. In severe cases, it can suppurate, forming a subungual abscess, which may require incision and drainage, making treatment quite troublesome and painful.
What are the correct steps to remove a hangnail?
The key to properly treating hangnails is to avoid using force, use tools, and remove them gently. The first step is to soften the hangnail. Soak your fingers in warm water for about 5 minutes, or apply a warm, damp towel to your fingers. This will soften the dry, raised cuticle, reducing resistance during removal. The second step is to disinfect and trim the tools. Use a sharp pair of nail clippers or small curved-tipped scissors that have been carefully wiped with an alcohol swab. Do not use regular nail clippers, as they are not sharp enough and can easily cause squeezing and secondary tearing. The third step is precise trimming. Gently pinch the raised part of the hangnail and, using a disinfected tool, neatly trim it along the base. Be steady and only trim the raised part; never pull or cut too deep and damage the underlying healthy skin. The fourth step is disinfection and moisturizing. After trimming, use a cotton swab to apply a small amount of iodine solution to the small wound for disinfection. After the disinfectant has dried completely, immediately apply a rich hand cream or petroleum jelly and gently massage the skin around the nails to replenish its oils and moisture. This is a key step in preventing hangnails from recurring.
How to effectively prevent hangnails from recurring?
The core strategy for preventing hangnails is to combat dryness and strengthen hydration. Develop a habit of using hand cream regularly , especially after washing hands, doing housework, or contact with water or detergents. Choose products containing moisturizing and repairing ingredients such as urea, ceramides, glycerin, and squalane for better hydration of the skin around the nails. When doing housework such as washing dishes or laundry, wear rubber gloves to reduce direct damage to the skin barrier from chemicals and moisture. Regularly soak your fingers in warm water and gently massage your hands and nail edges with a gentle exfoliating product (such as a glycolic acid or salicylic acid body lotion) to help remove dead skin cells, but do not do this too frequently; once or twice a week is sufficient. Break the bad habit of biting your nails or picking at the edges of your nails, as these actions themselves cause mechanical damage. In terms of diet, pay attention to supplementing with B vitamins and vitamin A, which are beneficial for maintaining healthy skin. If hangnails occur unusually frequently or persistently, and are accompanied by other skin problems, consider whether there is a deficiency in certain nutrients or a skin condition (such as hand eczema), in which case consult a dermatologist.
For more information on Innomed®Silicone Foam Dressing, Refer to the Previous Articles. If you have customized needs, you are welcome to contact us; You Wholeheartedly. At longterm medical, we transform this data by Innovating and Developing Products that Make Life easier for those who need loving care.
Editor: kiki Jia

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体








