How to choose the right bandages for your family members?
Most family medicine cabinets keep a few rolls of bandages, but are you aware that different bandages can play vastly different roles in critical situations? Choosing the wrong ban...
| Reorder No. | size | Quantity |
| G3121 | 2''×2'' (5cm×5cm) | 10/10/Cs |
| G3122 | 4''×4'' (10cm×10cm) | 10/10/Cs |
| G3123 | 4''×8'' (10cm×20cm) | 10/10/Cs |
| G3124 | 6''×6'' (15cm×15cm) | 10/10/Cs |
| G3126 | 2.7''×4.3'' (7cm×11cm) | 10/10/Cs |
| G3127 | 8''×8'' (20cm×20cm) | 10/10/Cs |
| G3128 | 3''×3'' (7.5cm×7.5cm) | 10/10/Cs |
| G3129 | 4''×7'' (10cm×17.5cm) | 10/10/Cs |
|
Product Code: |
|
|
With edge |
|
|
7.5cm×7.5cm |
S72033 |
|
10cm×10cm |
S72044 |
|
10cm×20cm |
S72048 |
|
10cm×30cm |
S72412 |
|
12.5cm×12.5cm |
S72055 |
|
15cm×15cm |
S72066 |
|
15cm×20cm |
S72068 |
|
20cm×20cm |
S72088 |
|
Without edges. |
|
|
5cm×5cm |
S71022 |
|
7.5cm×7.5cm |
S71033 |
|
10cm×10cm |
S71044 |
|
10cm×20cm |
S71048 |
|
12.5cm×12.5cm |
S71055 |
|
15cm×15cm |
S71066 |
|
15cm×20cm |
S71068 |
|
20cm×20cm |
S71088 |

Zhejiang Longterm Medical is a well-known China PU Foam Dressing suppliers and OEM PU Foam Dressing Company, specializing in the research and development, production and sales of high-end medical dressings. Our PU Foam Dressing have passed the US FDA certification, German TUV ISO13485 certification, CE certification.
Founded in 2012
Land area
Production capacity
National Patent
Most family medicine cabinets keep a few rolls of bandages, but are you aware that different bandages can play vastly different roles in critical situations? Choosing the wrong ban...
In pet-owning households, besides the usual iodine and cotton swabs, a roll of pet-specific self-adhesive elastic bandage is definitely a hidden gem in the first-aid kit. It's far ...
Tetanus is a serious infectious disease caused by Clostridium tetani, a bacterium widely found in soil, dust, and animal feces. Not all wounds require a tetanus shot; vaccination d...
Infection and inflammation are two closely related but fundamentally different concepts in wound care. Correctly distinguishing between them is crucial for wound assessment and tre...
Pressure ulcers are skin and subcutaneous tissue injuries caused by prolonged pressure on localized areas, and are common in people with limited mobility. Proper dressing changes a...
Hello everyone, today I'll share two commonly used auxiliary methods for dressing changes: soaking and wet compresses. Although they sound simple, using them correctly can greatly ...
Wound dehiscence is a worrying situation during postoperative or traumatic recovery, especially when patients see previously closed incisions or wounds reopening, often causing anx...
Wound healing is a dynamic process, and changes in the color of the wound surface directly reflect the healing stage and potential problems. Learning to observe and distinguish dif...
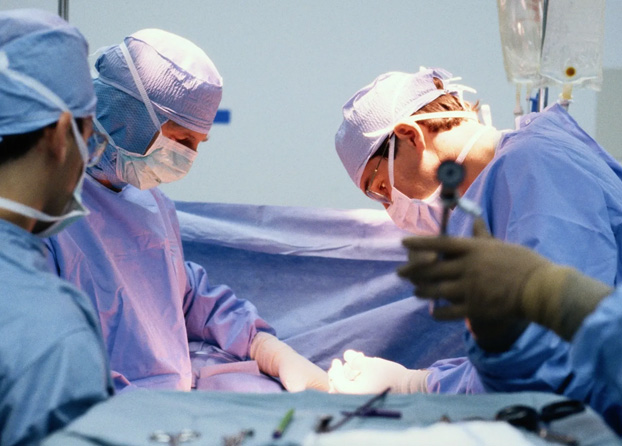
Our solutions start with a need. Patients and healthcare professionals inspire us to design medical solutions for wound management, surgery and pressure ulcer prevention. We want to enhance performance at every point of care – from the operating room to the home.
 Address
AddressOffice:No. 277, Shuangshan Road, Deqing County, Huzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
 Phone
PhonePhone:0086 15157187579
 Email
EmailEmail:export@longterm-health.com
 Manager
ManagerManager: Wendy shi
 Telephone
TelephoneTelephone: 0086-571-88160893